
Why Organic B2B Lead Generation Matters
In today’s hyper-competitive B2B landscape, generating leads efficiently and cost-effectively has become more critical than ever.
With buyer journeys becoming longer and decision-makers more discerning, businesses can no longer afford to rely solely on expensive ad-driven strategies.
The rising cost-per-lead and declining ROI from paid ads are pressing concerns—especially for companies aiming to scale sustainably.
Paid media is not dead—but it’s certainly not the most efficient starting point. As ad fatigue grows and platforms become saturated, many businesses are turning toward organic strategies to attract B2B leads that are not only cost-effective but also higher in quality.
So, how can you generate B2B leads organically and still compete with big-budget players?
That’s where Digitechniks comes in. As a trusted B2B lead generation agency in India, we specialize in helping businesses—especially in tech, SaaS, consulting, and services—generate inbound leads using zero-ad-spend strategies.
From our base in Bangalore, we’ve helped clients across industries build sustainable sales pipelines through content marketing, LinkedIn outreach, SEO, and email automation.
We’ve seen firsthand that qualified leads generated through organic channels are more likely to convert and stick around—because they’re nurtured through value, not persuasion. These leads are informed, interested, and better aligned with your solutions from the very beginning.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through our proven, practical strategies to build and scale your lead funnel without spending a rupee on ads.
These are the same methods we’ve used to generate 3–5 qualified meetings per week for clients—consistently.
Let’s explore how a smarter, organic-first approach to B2B lead generation can give your business the edge it needs in 2025 and beyond.
Key Takeaways:
-
Paid ads are not the only way – With rising costs, zero-ad-spend strategies are proving to be more sustainable and effective for generating quality B2B leads.
-
Trust grows organically – Content marketing, SEO, LinkedIn outreach, and case studies help build authority and credibility over time, which paid ads alone can’t achieve.
-
Lead nurturing matters – Organic strategies engage prospects at every stage of the buyer journey, making conversions smoother and more consistent.
-
A structured process delivers results – The Digitechniks framework, from understanding the business to defining buyer personas and targeting on LinkedIn, has shown consistent success, bringing in 3–5 qualified meetings each week.
-
LinkedIn automation is a game-changer – When done with personalization and value-driven messaging, it increases acceptance and meeting rates significantly.
-
Cold email strengthens the pipeline – Verified contact lists combined with multi-step personalized sequences create a predictable flow of opportunities without relying on ads.
-
Organic strategies keep working – Unlike paid campaigns that stop once the budget ends, organic content, SEO, and outreach continue generating leads long after they’re set up.
What is B2B Lead Generation?
B2B lead generation is the process of attracting and capturing the interest of business decision-makers—like CXOs, managers, or procurement heads—with the goal of converting them into potential clients.
Unlike B2C, where individual consumers are the target, B2B leads involve companies and professionals looking for solutions that solve business problems.
It’s not just about getting more contacts—it’s about finding the right-fit companies who are more likely to engage, convert, and grow with your business.
Whether through LinkedIn outreach, SEO content, or cold email, the goal is to bring qualified prospects into your sales funnel and move them closer to a buying decision.
What Are B2B Leads and Demand Generation?
B2B leads are potential business clients who have shown interest in your product or service—whether through a website visit, form submission, or social engagement.
B2B demand generation goes a step further, focusing on creating awareness and nurturing interest in your offering before a lead even enters your sales funnel.
The goal isn’t just to collect contact details—it’s to attract qualified leads who are a strong match for your ideal customer profile and are likely to convert into paying clients.
MQL vs SQL: Why the Difference Matters
Not all leads are created equal. A Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL) is someone who has engaged with your content or campaigns, while a Sales Qualified Lead (SQL) has shown intent and readiness to buy—making them a priority for your sales team.
Focusing your strategy on Sales Qualified Leads ensures that your pipeline is filled with high-potential prospects, not just random contacts. This alignment between marketing and sales is what drives real revenue growth in B2B.
Why Organic Strategies Are Essential for B2B Lead Generation in 2025
In 2025, the rules of B2B lead generation have changed. As businesses face rising ad costs and shrinking engagement rates, the focus is shifting toward zero-ad-spend strategies that deliver qualified leads through organic channels. With decision-makers becoming more selective and content-saturated markets demanding authenticity, organic lead generation isn’t just an option—it’s a competitive advantage.
Key Reasons Why Organic Matters:
- Content Saturation is Real: Buyers are overwhelmed with ads. Organic content cuts through the noise by offering genuine value.
- Rising Ad Costs = Lower ROI: Paid campaigns are expensive and often unsustainable for long-term growth. Organic methods offer higher ROI over time.
- Buyer Trust is Built, Not Bought: Organic touchpoints like SEO blogs, case studies, and LinkedIn conversations build credibility and trust gradually.
- Better Lead Nurturing: Organic strategies naturally support lead nurturing by engaging prospects at each stage of their buying journey.
- More Qualified Leads: Leads generated organically tend to be more informed and aligned with your offerings—leading to better conversions.
- Sustainable Growth Engine: Unlike ads that stop when the budget stops, organic strategies compound and generate long-term pipeline value.
If you’re wondering how to generate qualified leads for B2B businesses without blowing your budget, organic is your answer—and 2025 is the year to double down on it.
Digitechniks Proven Method for Organic B2B Lead Generation
At Digitechniks, we follow a structured, research-driven process to generate qualified B2B leads organically. Every step is built to align with your unique value proposition and attract the right decision-makers into your sales funnel—without paid ads.
Step 1: Comprehensive Business Understanding
Before launching any outreach, we start with a deep dive into your business model, goals, and target audience. Our detailed client questionnaire uncovers your Unique Value Proposition (UVP), helping us craft hyper-relevant messaging.
- Helps identify your best-fit leads and tailor content around buyer needs
- Forms the foundation for a well-aligned sales funnel
- Supports B2B lead generation with clarity and precision
Step 2: Creating Targeted Buyer Personas
We build Buyer Personas based on demographic and psychographic data, roles, pain points, and buying behavior. This ensures your message resonates with actual decision-makers—those with the authority and intent to buy.
- Improves lead nurturing with more personalized, relevant messaging
- Focuses on qualified leads by addressing specific business challenges
- Supports targeting CXOs, VPs, and Marketing Heads with tailored content
Step 3: Defining LinkedIn Targeting Parameters
LinkedIn remains the most powerful platform for B2B outreach. We define filters like company size, industry, and job titles to precisely connect with your ideal clients—ensuring efficient and scalable outreach.
- Criteria include: 11–50 employee companies, decision-makers in IT/Services
- Supports LinkedIn lead generation by narrowing outreach to high-potential contacts
- Enables messaging that’s specific, relevant, and conversion-optimized
This method has helped our clients consistently generate 3–5 qualified meetings per week—all through an organic, zero-ad-spend approach.
Proven Organic Lead Generation Strategies (Zero Ad Spend)

Strategy 1: LinkedIn Automated Outreach
Objective:
Generate qualified meetings with IT service decision-makers (CXOs, Directors, VPs) via LinkedIn automation.
Process:
- Connected the CEO’s LinkedIn profile with LinkedIn Sales Navigator and LinkedIn Helper.
- Built a segmented list based on company size, job titles, and industry (IT services).
- Sent personalized connection requests followed by automated, value-focused follow-ups.
- Execute automated follow-up sequences spaced over 7–10 days.
- Include weekly nurturing messages prompting recipients to book a discovery call.
Results:
- Successfully generating 3–5 qualified meetings weekly.
- Increased profile visibility and engagement from decision-makers.
- Improved conversion rate from connection to booked call by 22%.
For a comprehensive guide on maximizing LinkedIn outreach using automation strategies, see our detailed article on LinkedIn Automated Outreach: Proven Blueprint for Generating B2B Leads.
Strategy 2: Cold Email Outreach
(Complementary Method)
Objective:
Reach decision-makers directly via personalized cold email sequences to generate qualified B2B leads.
Process:
- Extracted verified email addresses using LinkedIn targeting filters and tools like Snov.io.
- Developed multi-step email sequences with personalized subject lines and pain-point-driven content.
- Used automation tools to manage follow-ups, spacing them to maximize open and reply rates.
- Included CTAs leading to a discovery call or calendar booking.
Results:
- Generated 1–2 additional qualified meetings weekly.
- Achieved a 15–18% email response rate.
- Nurtured cold leads into active sales conversations without ad spend.
Read also: Cold Email Outreach Blueprint: Proven Method to Generate High-Quality B2B Leads in 2025
Strategy 3: SEO-Driven Case Studies for Inbound Organic Traffic
Objective:
Drive inbound leads through high-ranking SEO-optimized case studies targeting informational keywords.
Process:
- Identified high-intent keywords aligned with B2B search behavior (e.g., “pipeline building strategies”).
- Created detailed, story-driven case studies showcasing measurable results and strategic insights.
- Optimized on-page SEO with internal links, schema, and metadata for discoverability.
- Promoted via LinkedIn posts, newsletters, and communities to boost visibility and backlinks.
Results:
- Case studies began ranking on Page 1 of Google within 60–90 days.
- Brought in consistent inbound leads through organic search.
- Strengthened brand authority and improved site engagement metrics.
Read more: Ultimate Guide to SEO for B2B Lead Generation in 2025: Proven Strategy & Best Practices
Real Case Study: LinkedIn Automated Outreach
How a B2B Consultant Generated 30–50 Qualified Meetings Per Month Using LinkedIn Automated Outreach & Cold Email
Objective:
To generate qualified meetings with decision-makers (CXOs, Directors, VPs) from IT services companies using LinkedIn automation—without relying on paid ads.
Approach:
- Used client’s LinkedIn profile integrated with Sales Navigator and LinkedIn Helper.
- Defined targeting criteria: Company size (11–50 employees), Industry (IT services), and Job Titles (CXOs, Directors, VPs).
- Sent personalized connection requests with customized intro messages.
- Executed automated follow-ups over 7–10 days to warm up leads.
- Final nurturing messages encouraged prospects to book discovery calls.
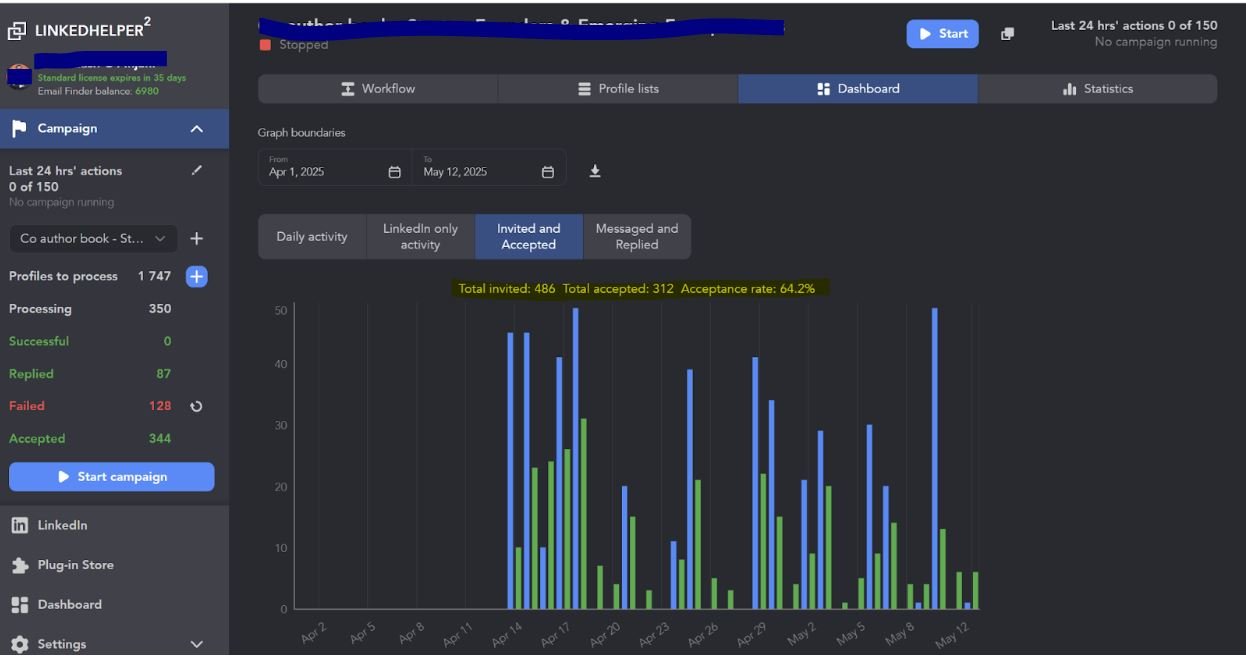
Results:
- Total Invitations Sent: 486
- Connections Accepted: 312
- Acceptance rate: 64.2%
- Meeting Booked: 33
- Conversion Rate from Connection to Meeting: 10.57%
Real Case Study: Cold Email Outreach
Objective:
Generate qualified B2B meetings with CXOs & senior decision-makers organically.
Approach:
- Extracted verified B2B emails using LinkedIn filters and tools like Snov.io.
- Built segmented lists targeting CXOs, and other decision-makers based on industry, company size, and decision-making role.
- Crafted 3-step cold email sequence: initial outreach + 2 strategic follow-ups.
- Personalized each email based on role, pain point, and business objective.
- Used scheduling tool (e.g., Calendly) as the CTA in final email.
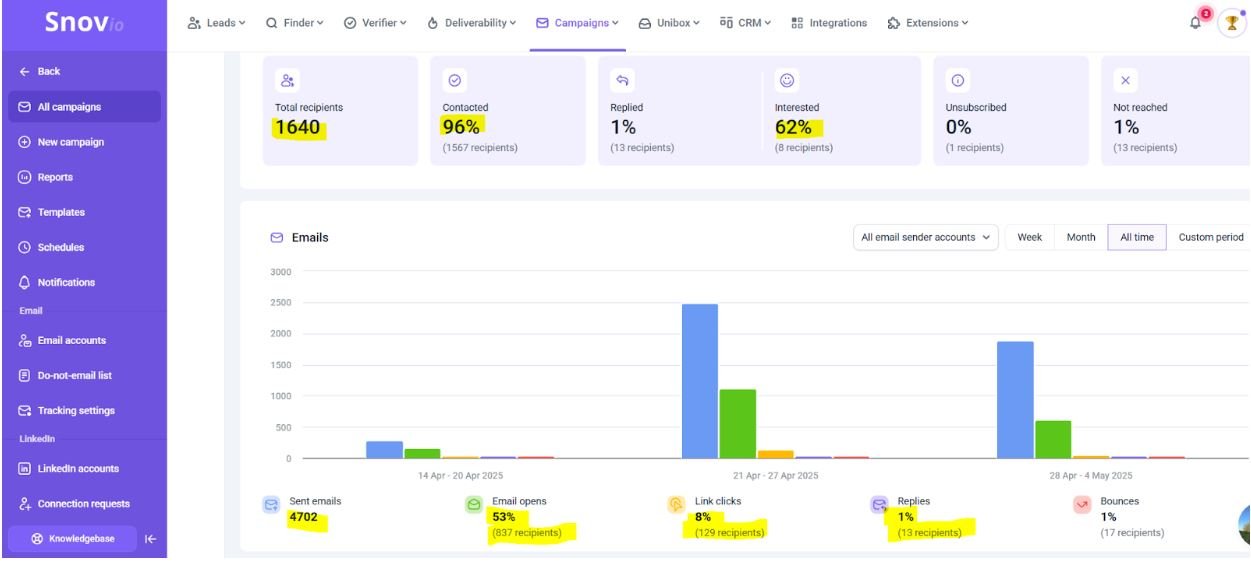
Results:
- Emails Sent: 4702
- Open Rate: 53%
- Reply Rate: 8%
- Meetings Booked: 32
Looking to further boost your LinkedIn lead generation results?
Explore our proven LinkedIn Automated Outreach Blueprint to start scaling your outreach today.
Key Advanced Strategies for Organic B2B Lead Generation in 2025
In 2025, B2B lead generation is no longer about just showing up—it’s about showing up smart. Businesses that leverage AI and distribute content across multiple platforms are outperforming those who rely on outdated, single-channel tactics. If you’re serious about staying ahead of the curve and attracting qualified leads, here’s what to focus on next:
Leverage AI for Personalization and Automation
Use AI tools to craft hyper-personalized content, email sequences, and LinkedIn messages that speak directly to each lead’s industry, role, and challenges.
Automate follow-ups and segmentation to scale nurturing without losing relevance.
Multi-Channel Content Distribution
Don’t rely on just LinkedIn or email. Share educational content via YouTube, niche Slack groups, Reddit threads, or industry forums.
This builds visibility and trust in different digital neighborhoods where your audience spends time.
Behavior-Based Lead Scoring and Retargeting
Use behavior triggers like page visits, video views, or email clicks to assign lead scores.
Retarget warm leads with customized content based on their interests and stage in the funnel.
By implementing these AI-powered, multichannel, and insight-driven strategies, you’ll not only generate more leads—you’ll attract the right ones and move them through the funnel faster.
Read also: How to Build a T-Model Pitch for B2B Lead Generation That Converts Cold Emails into Sales Meetings
Conclusion & Actionable Next Steps
In today’s digital-first world, relying solely on paid ads for B2B leads is no longer sustainable. As you’ve seen through real-life results and proven strategies, B2B lead generation with zero ad spend is not only possible—it’s more efficient and scalable.
From personalized LinkedIn outreach to cold emails and SEO-driven case studies, organic strategies help attract qualified leads who are genuinely interested in what you offer. And when done right, they build trust, authority, and long-term growth.
👉 Ready to implement a zero-ad-spend B2B lead system tailored to your business?
Book Your Free Discovery Call with Digitechniks and let’s map out your next steps toward predictable, cost-effective lead generation.
FAQs
What is zero-budget B2B lead generation?
Zero-budget B2B lead generation refers to attracting business leads without spending on paid ads. It relies on organic strategies like LinkedIn outreach, SEO content, cold emailing, and lead nurturing to build a qualified sales pipeline.
Can you really generate leads with zero budget?
Yes. By leveraging LinkedIn, email outreach, organic SEO, and referrals, you can build a strong pipeline without ad spend.
What is the best free lead generation method?
LinkedIn outreach combined with personalized cold emails is one of the most effective free strategies.
How can I generate B2B leads organically?
You can generate B2B leads organically through methods like creating SEO-optimized content, engaging decision-makers on LinkedIn, running cold email campaigns, and building case studies that attract inbound traffic.
Which platform is best for organic B2B lead generation?
LinkedIn is considered the most effective platform for organic B2B lead generation due to its professional targeting options, content reach, and ability to connect directly with decision-makers.
What are the benefits of organic lead generation over paid ads?
Organic lead generation is more sustainable and cost-effective. It builds long-term trust, attracts more qualified leads, and delivers higher ROI compared to paid ads that stop working once the budget runs out.
Can cold email outreach still work in 2025?
Yes, when personalized and automated strategically, cold email outreach remains an effective channel for generating high-quality B2B leads—even in 2025.
How long does zero-budget lead generation take?
Typically 4–8 weeks, depending on your consistency in outreach and content creation.

Sharan Kulkarni
Sharan Kulkarni is a B2B Lead Generation Specialist and author of ROI Decoder, with 10+ years’ experience helping SaaS, IT, and service firms generate predictable qualified leads. He leads Digitechniks’ outreach strategies across LinkedIn, cold email, and SEO. Connect with Sharan on LinkedIn



